Google Search Console API

Table of Contents
Introduction
Google Search Console is a free web service provided by Google. It helps you monitor, manage, and improve how your website appears in Google Search results.
Simply put, it's a communication tool that connects your website with Google Search.
While Google Search Console allows you to check the indexing status (whether your website's pages are correctly recognized by Google) on a URL-by-URL basis, Google Search Console also provides an API, allowing you to check the indexing status programmatically.
The steps are summarized below.
Prerequisites
- You must have a Google Cloud Platform (GCP) account. The Google Search Console API is an API provided by GCP.
- Your website must be registered with Google Search Console.
Preparing to use the API
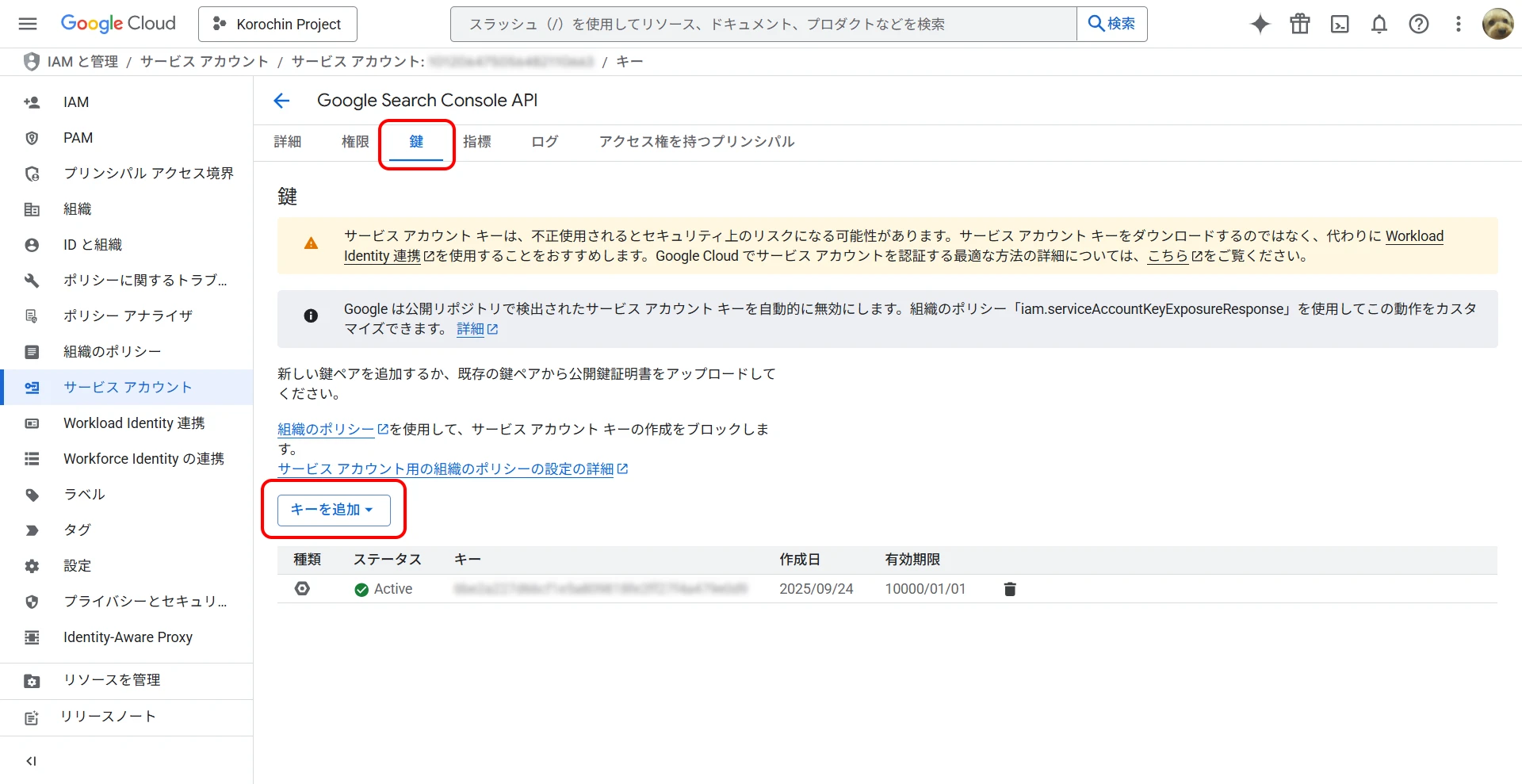
1Enable the API
From the GCP menu, select APIs & Services > Library.
Search for "Google Search Console API" in the search bar and enable it (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Google Search Console API `
`
2Create a Service Account
From the GCP menu, navigate to IAM & Admin > Service Accounts.
Click "Create Service Account", enter an account name, and create it. No additional permissions are required.
Figure 2. Create a Service Account `
`
3Create a Key
Click "Add Key" on the "Keys" tab of the created service account (Figure 3), select JSON as the key type, and download it. The JSON file will be used for API calls from your program. This JSON file contains credentials for accessing the API, so please keep it secure.
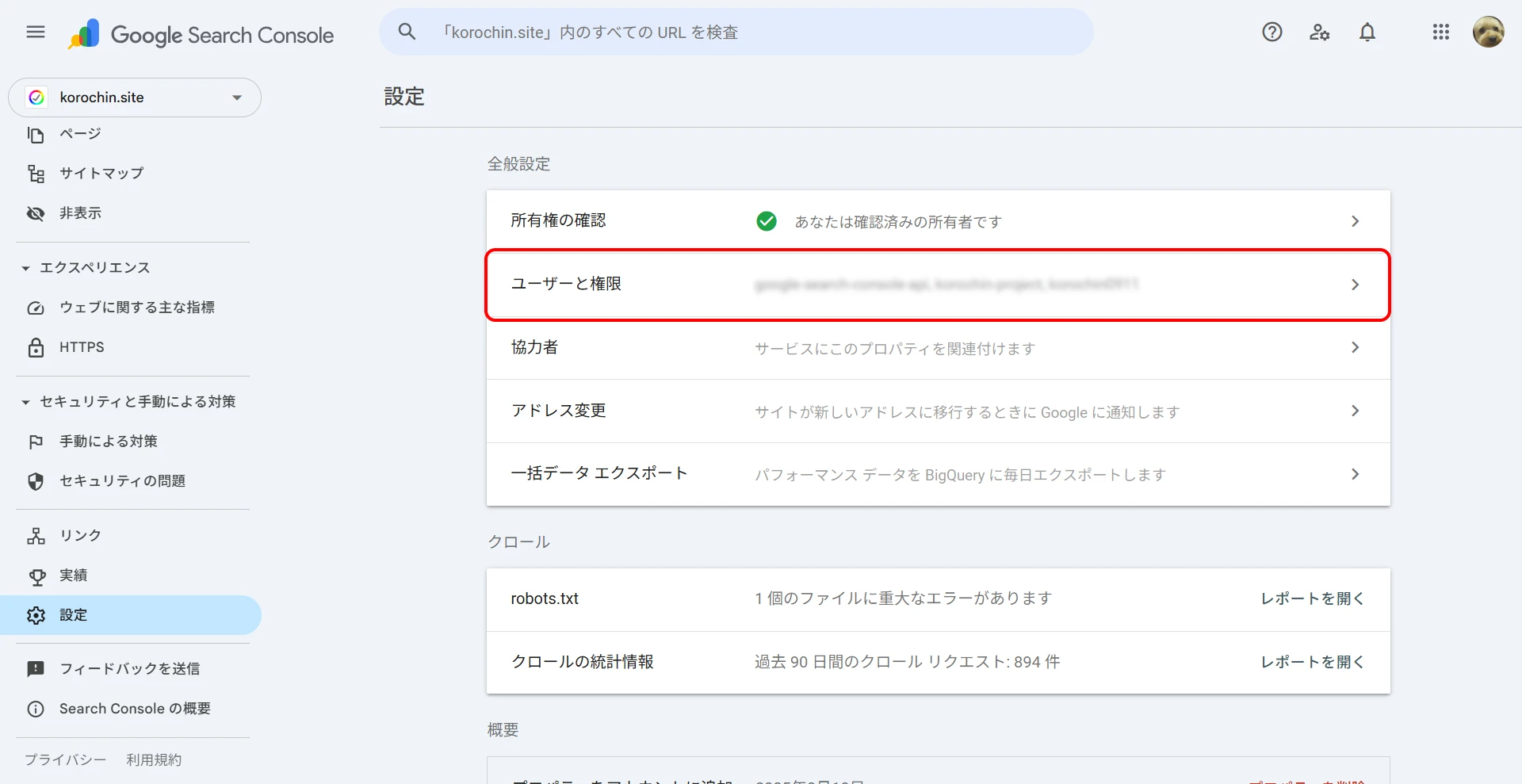
4Add the Service Account to Google Search Console
Next, access Google Search Console and configure the service account created in "2. Create a Service Account".
From Settings > Users and permissions, click "Add user" and add the email address of the service account created in "2. Create a Service Account". "Restricted" permission is sufficient.
Calling the API from a Program
Now you are ready to call the API using a programming language. The URL Inspection API used here uses a POST request, and you specify the URL to inspect and the site URL in JSON format in the request body.
- API endpoint:
https://searchconsole.googleapis.com/v1/urlInspection/index:inspect - Example JSON POST:
{
"inspectionUrl": "https://www.example.com/mypage",
"siteUrl": "https://www.example.com/",
"languageCode": "en-US"
}
Be careful with how siteUrl is specified.
Figure 5. Select Property Type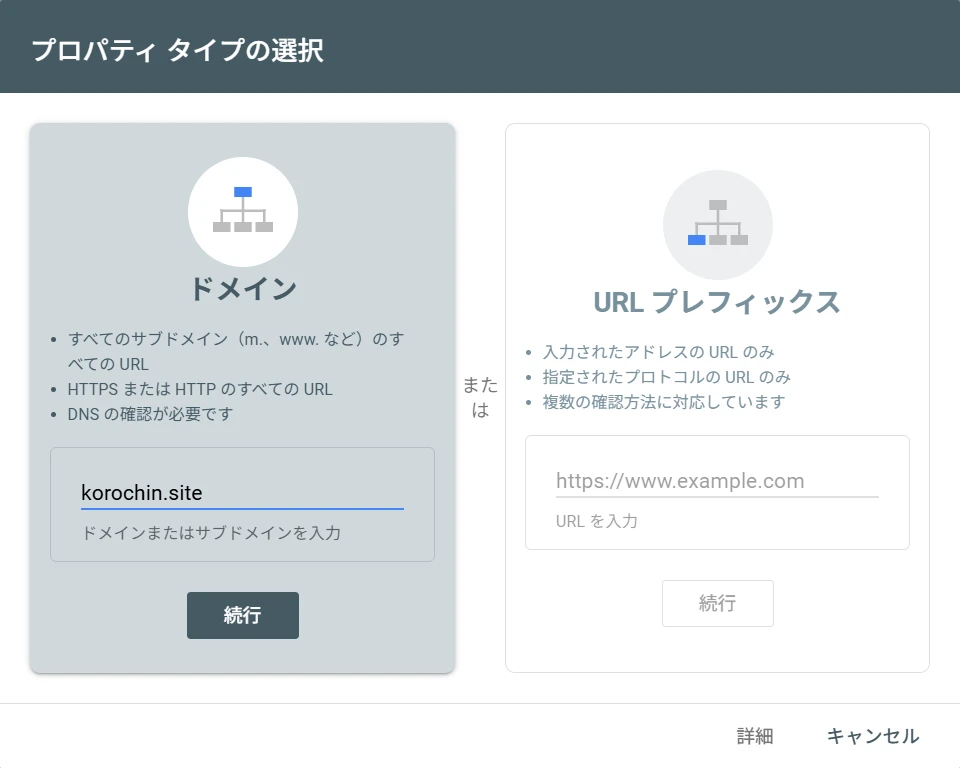
If you specified "Domain" when adding a Search Console property, as shown in Figure 5, siteUrl must be in the format sc-domain:domain_name.
In the example above, specifying https://korochin.site will result in a "You do not own this site" error.
<HttpError 403 when requesting https://searchconsole.googleapis.com/v1/urlInspection/index:inspect?alt=json returned "You do not own this site, or the inspected URL is not part of this property.". Details: "You do not own this site, or the inspected URL is not part of this property.">
For Python
Install the library for working with Google APIs in Python.
pip install google-api-python-client google-auth-httplib2 google-auth-oauthlib
Place the downloaded JSON credentials file in the same directory as your py file.
The filename is search_console_credentials.json.
import json
import googleapiclient.discovery
import google.auth
CREDENTIALS_FILE = "search_console_credentials.json"
try:
# Load credentials
credentials, _ = google.auth.load_credentials_from_file(
CREDENTIALS_FILE, ["https://www.googleapis.com/auth/webmasters.readonly"]
)
# Build the Google Search Console API service
service = googleapiclient.discovery.build(
"searchconsole", "v1", credentials=credentials
)
# Create the request body
site_url = "sc-domain:korochin.site"
inspection_url = "https://korochin.site/articles/visual-studio-2026-insiders"
request_body = {
"inspectionUrl": inspection_url,
"siteUrl": site_url,
"languageCode": "ja",
}
# Call the API
response = service.urlInspection().index().inspect(body=request_body).execute()
print(json.dumps(response, indent=2))
except Exception as e:
print(f"エラーが発生しました: {e}")
If you want to send a request directly without using googleapiclient.discovery, the code would look like this.
import json
import requests
import google.auth
from google.auth.transport.requests import Request
CREDENTIALS_FILE = 'search_console_credentials.json'
# Load credentials
credentials, _ = google.auth.load_credentials_from_file(
CREDENTIALS_FILE,
scopes=['https://www.googleapis.com/auth/webmasters.readonly']
)
# Refresh the authentication token
credentials.refresh(Request())
# Set API endpoint and request headers
api_url = 'https://searchconsole.googleapis.com/v1/urlInspection/index:inspect'
headers = {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'Authorization': f'Bearer {credentials.token}'
}
# Create the request body
site_url = 'sc-domain:korochin.site'
inspection_url = 'https://korochin.site/articles/visual-studio-2026-insiders'
request_body = {
'inspectionUrl': inspection_url,
'siteUrl': site_url,
'languageCode': 'ja'
}
# Execute HTTP POST request
try:
response = requests.post(api_url, headers=headers, data=json.dumps(request_body))
response.raise_for_status() # Raise an exception if the status code is not in the 2xx range.
print(json.dumps(response.json(), indent=2))
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
print(f"エラーが発生しました: {e}")
For C#
Similar to Python, place the credentials file in the same directory as your application's executable file.
Use two packages.
dotnet add package Google.Apis.Auth
dotnet add package Google.Apis.SearchConsole.v1
or
Install-Package Google.Apis.Auth
Install-Package Google.Apis.SearchConsole.v1
using Google.Apis.Auth.OAuth2;
using Google.Apis.SearchConsole.v1;
using Google.Apis.SearchConsole.v1.Data;
using Google.Apis.Services;
// Load credentials
var credentialsPath = "search_console_credentials.json";
using var stream = new FileStream(credentialsPath, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read);
var credential = GoogleCredential.FromStream(stream)
.CreateScoped([SearchConsoleService.Scope.WebmastersReadonly]);
// Generate Search Console API service
using var service = new SearchConsoleService(new BaseClientService.Initializer
{
HttpClientInitializer = credential,
});
// Create request body
var siteUrl = "sc-domain:korochin.site";
var inspectionUrl = "https://korochin.site/articles/visual-studio-2026-insiders";
var request = new InspectUrlIndexRequest
{
InspectionUrl = inspectionUrl,
SiteUrl = siteUrl,
LanguageCode = "ja"
};
try
{
// Call the API
var response = await service.UrlInspection.Index.Inspect(request).ExecuteAsync();
Console.WriteLine(response.InspectionResult.IndexStatusResult.IndexingState);
}
catch (Google.GoogleApiException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"エラーが発生しました: {ex.Message}");
}
API Response Data
The response data is in the following format. For detailed specifications, please refer to the official documentation in the references.
{
"inspectionResult": {
"inspectionResultLink": "https://search.google.com/search-console/inspect?resource_id=sc-domain:korochin.site&id=hogehogeA&utm_medium=link&utm_source=api",
"indexStatusResult": {
"verdict": "PASS",
"coverageState": "送信して登録されました",
"robotsTxtState": "ALLOWED",
"indexingState": "INDEXING_ALLOWED",
"lastCrawlTime": "2025-09-24T04:12:40Z",
"pageFetchState": "SUCCESSFUL",
"googleCanonical": "https://korochin.site/articles/visual-studio-2026-insiders",
"crawledAs": "MOBILE"
},
"mobileUsabilityResult": {
"verdict": "VERDICT_UNSPECIFIED"
}
}
}
The indexing status is set in indexingState. The meaning of each status is shown in the table below. INDEXING_ALLOWED indicates that indexing is allowed.
| Status Name | Description |
|---|---|
| INDEXING_STATE_UNSPECIFIED | The indexing status is unknown. |
| INDEXING_ALLOWED | Indexing is allowed. |
| BLOCKED_BY_META_TAG | Indexing is not allowed. "noindex" was detected in the robots meta tag. |
| BLOCKED_BY_HTTP_HEADER | Indexing is not allowed. "noindex" was detected in the X-Robots-Tag HTTP header. |
| BLOCKED_BY_ROBOTS_TXT | Reserved. Currently not in use. |